By American April 3, 2025
In today’s digital age, credit card processing has become an integral part of conducting business transactions. However, like any technology, credit card processing systems are not immune to occasional outages. These outages can have a significant impact on businesses, causing financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. Understanding why credit card processing outages occur and how to mitigate their effects is crucial for businesses to maintain smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
The Impact of Credit Card Processing Outages on Businesses
Credit card processing outages can have severe consequences for businesses of all sizes. When a business relies heavily on credit card transactions, an outage can disrupt its ability to accept payments, resulting in lost sales and revenue. According to a study conducted by Javelin Strategy & Research, businesses can lose an average of $4,700 per minute during a credit card processing outage. This loss can quickly add up, especially for larger businesses with high transaction volumes.
Moreover, credit card processing outages can damage a business’s reputation. Customers expect seamless payment experiences, and any disruption can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction. In today’s competitive market, where customer loyalty is paramount, a negative experience caused by an outage can drive customers away and tarnish a business’s image. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to understand the common causes of credit card processing outages and take preventive measures to minimize their impact.
Common Causes of Credit Card Processing Outages
Credit card processing outages can occur due to various reasons, ranging from technical glitches to external factors. Understanding these common causes can help businesses identify potential vulnerabilities and take proactive measures to prevent outages. Some of the most common causes of credit card processing outages include:
1. Network Connectivity Issues: One of the primary causes of credit card processing outages is network connectivity problems. If the connection between the business’s point-of-sale (POS) system and the payment processor is disrupted, transactions cannot be processed. Network outages can be caused by issues with internet service providers, hardware failures, or even natural disasters.
2. Software Bugs and Updates: Software bugs and updates can also lead to credit card processing outages. When payment processing software is not properly tested or updated, it can result in system failures or errors. In some cases, incompatible software updates can cause conflicts and disrupt the payment processing flow.
3. Hardware Failures: Hardware failures, such as malfunctioning card readers or POS terminals, can also cause credit card processing outages. If the hardware components responsible for processing payments are not functioning correctly, transactions cannot be completed. Regular maintenance and monitoring of hardware can help identify potential issues before they cause outages.
4. Cybersecurity Attacks: In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity attacks pose a significant threat to credit card processing systems. Hackers may attempt to breach the system and steal sensitive customer information or disrupt payment processing operations. A successful cyber attack can lead to system downtime and compromise the security of customer data.
5. Third-Party Service Provider Issues: Many businesses rely on third-party service providers for credit card processing. If these service providers experience technical issues or outages, it can directly impact the business’s ability to process payments. It is essential for businesses to choose reliable service providers and have contingency plans in place in case of service disruptions.
How Credit Card Processing Systems Work: A Comprehensive Overview
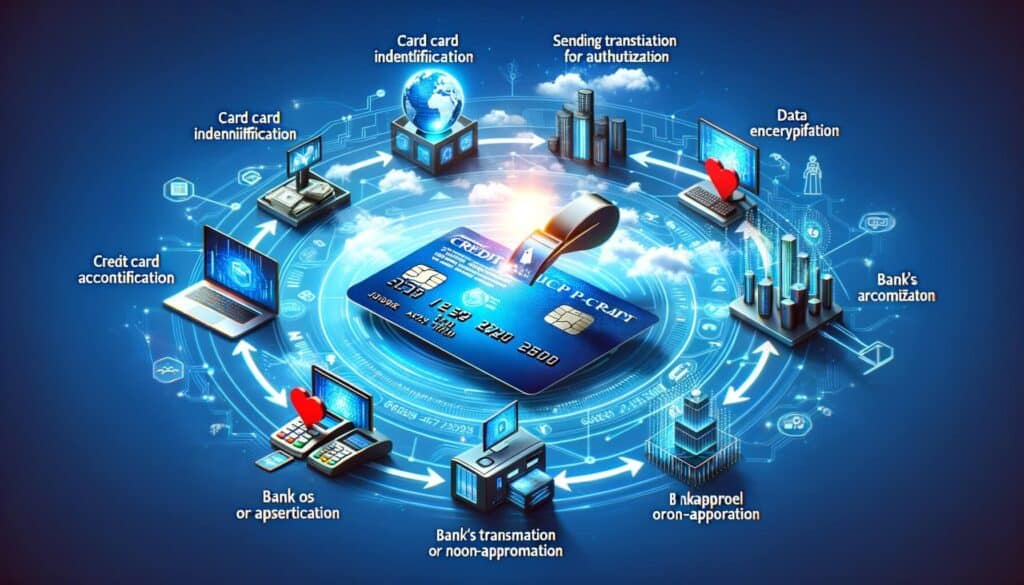
To understand credit card processing outages better, it is essential to have a comprehensive overview of how credit card processing systems work. The process involves several steps, from the moment a customer swipes or inserts their card to the final authorization and settlement of the transaction. Understanding this process can help businesses identify potential points of failure and take preventive measures.
1. Card Present Transactions: In a card present transaction, the customer physically presents their credit card to the merchant. The merchant swipes or inserts the card into a card reader, which reads the card’s magnetic stripe or chip. The card reader then encrypts the card data and sends it to the payment processor for authorization.
2. Card Not Present Transactions: In a card not present transaction, the customer provides their credit card information without physically presenting the card. This can occur in online or over-the-phone transactions. The merchant enters the card information into a secure payment gateway, which encrypts the data and sends it to the payment processor for authorization.
3. Authorization: Once the payment processor receives the card data, it sends a request to the card issuer for authorization. The card issuer verifies the cardholder’s information, checks for available funds, and determines whether the transaction should be approved or declined. The authorization response is then sent back to the payment processor.
4. Settlement: After the transaction is authorized, the settlement process begins. The payment processor sends the transaction details to the merchant’s acquiring bank, which initiates the transfer of funds from the cardholder’s account to the merchant’s account. The settlement process typically takes a few business days to complete.
Preventive Measures: Steps to Minimize the Risk of Outages
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate the risk of credit card processing outages, businesses can take several preventive measures to minimize their occurrence and mitigate their impact. By implementing these steps, businesses can ensure smoother operations and reduce the risk of financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
1. Redundant Network Connections: To minimize the impact of network connectivity issues, businesses can establish redundant network connections. This involves having multiple internet service providers or backup connections to ensure uninterrupted connectivity. Redundancy can help businesses maintain payment processing capabilities even if one network connection fails.
2. Regular Software Updates and Testing: Keeping payment processing software up to date is crucial for preventing outages caused by software bugs or compatibility issues. Businesses should regularly update their software and thoroughly test it before deploying it in a live environment. This helps identify and resolve any potential issues before they disrupt payment processing operations.
3. Hardware Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring of hardware components, such as card readers and POS terminals, can help identify and address potential failures before they cause outages. Businesses should establish maintenance schedules and perform routine checks to ensure hardware components are functioning correctly.
4. Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential for protecting credit card processing systems from cyber attacks. Businesses should invest in firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption technologies to safeguard sensitive customer data. Regular security audits and employee training can also help identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
5. Backup Payment Processing Solutions: In case of a credit card processing outage, having backup payment processing solutions can help businesses continue accepting payments. This can include alternative payment methods, such as mobile wallets or manual card imprinters, as well as contingency plans for offline transactions. Having backup solutions in place ensures that business operations can continue even during an outage.
What to Do During a Credit Card Processing Outage
Despite taking preventive measures, businesses may still experience credit card processing outages. In such situations, it is crucial to have a plan in place to minimize the impact on operations and customer satisfaction. Here are some steps businesses can take during a credit card processing outage:
1. Communicate with Customers: Promptly communicate with customers about the outage and provide alternative payment options, if available. This can include accepting cash, checks, or mobile payment methods. Clear and transparent communication helps manage customer expectations and minimize frustration.
2. Keep Records of Transactions: During an outage, it is essential to keep detailed records of all transactions attempted or completed. This documentation can be useful for reconciliation purposes once the system is back online. Businesses should also ensure that customer receipts are provided for future reference.
3. Monitor System Status: Continuously monitor the status of the credit card processing system to determine when it is back online. Regular updates from the payment processor or service provider can help businesses stay informed about the progress of resolving the outage.
4. Maintain Customer Service Support: Ensure that customer service support is available to address any concerns or questions from customers. This can help alleviate customer frustration and maintain a positive customer experience, even during an outage.
Troubleshooting Tips: Resolving Minor Credit Card Processing Issues
In some cases, businesses may encounter minor credit card processing issues that can be resolved without professional help. By following some troubleshooting tips, businesses can quickly identify and resolve these issues, minimizing downtime and disruption. Here are some common troubleshooting tips for resolving minor credit card processing issues:
1. Restart the System: Sometimes, a simple system restart can resolve minor software or connectivity issues. Restarting the POS system, card reader, or payment processing software can help refresh the system and restore normal functionality.
2. Check Network Connectivity: Verify that the network connection between the POS system and the payment processor is stable. Ensure that all cables are securely connected and that there are no issues with the internet service provider. Restarting the router or modem can also help resolve connectivity issues.
3. Update Software: Check for any available software updates for the payment processing software or card reader. Installing the latest updates can address known issues and improve system performance.
4. Clear Cache and Cookies: Clearing the cache and cookies on the web browser used for payment processing can help resolve issues related to stored data or temporary files. This can be done through the browser’s settings or preferences menu.
5. Contact Support: If the issue persists or is beyond the scope of troubleshooting, contact the payment processor or service provider’s support team. They can provide further guidance and assistance in resolving the issue.
When to Seek Professional Help: Dealing with Major Outages
While minor credit card processing issues can often be resolved through troubleshooting, major outages may require professional help. If businesses are unable to restore normal functionality or identify the root cause of the outage, it is advisable to seek assistance from experts. Here are some situations where professional help may be necessary:
1. Prolonged Downtime: If the credit card processing system remains offline for an extended period, it is crucial to involve professionals who can diagnose and resolve the issue. Prolonged downtime can result in significant financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
2. Complex Technical Issues: Some credit card processing outages may involve complex technical issues that require specialized knowledge and expertise to resolve. In such cases, professional assistance can help identify and address the underlying problem effectively.
3. Security Breaches: If a credit card processing outage is caused by a security breach or suspected unauthorized access, it is essential to involve cybersecurity experts. They can assess the extent of the breach, mitigate any potential damage, and implement measures to prevent future incidents.
4. Vendor or Service Provider Involvement: If the credit card processing system relies on third-party vendors or service providers, it may be necessary to involve their support teams. They can provide insights into the issue and work towards resolving it in collaboration with the business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Credit Card Processing Outages
Q1. What should I do if my credit card processing system goes down?
Answer: If your credit card processing system goes down, communicate with customers about the outage and provide alternative payment options, if available. Keep records of transactions, monitor the system status, and maintain customer service support. Troubleshoot minor issues, and if the problem persists or is beyond your expertise, seek professional help.
Q2. How can I prevent credit card processing outages?
Answer: To prevent credit card processing outages, establish redundant network connections, regularly update and test software, perform hardware maintenance and monitoring, implement robust cybersecurity measures, and have backup payment processing solutions in place.
Q3. How long do credit card processing outages typically last?
Answer: The duration of credit card processing outages can vary depending on the cause and complexity of the issue. Minor issues can often be resolved within a few minutes or hours, while major outages may take longer to resolve. Prolonged outages can result in significant financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
Q4. Can credit card processing outages be prevented entirely?
Answer: While it may not be possible to prevent credit card processing outages entirely, businesses can take preventive measures to minimize their occurrence and mitigate their impact. By implementing redundancy, regularly updating software, maintaining hardware, and investing in cybersecurity measures, businesses can reduce the risk of outages.
Q5. How can I ensure a smooth transition during a credit card processing outage?
Answer: To ensure a smooth transition during a credit card processing outage, communicate with customers, keep records of transactions, monitor the system status, maintain customer service support, and have backup payment processing solutions in place. Promptly resolving the outage and providing alternative payment options can help minimize disruption and maintain customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Credit card processing outages can have a significant impact on businesses, causing financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. Understanding the common causes of outages and taking preventive measures can help businesses minimize their occurrence and mitigate their effects. By establishing redundant network connections, regularly updating software, maintaining hardware, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, and having backup payment processing solutions, businesses can reduce the risk of outages.
In the event of an outage, clear communication with customers, record-keeping, and troubleshooting minor issues can help minimize disruption. Seeking professional help may be necessary for major outages or complex technical issues. By being proactive and prepared, businesses can navigate credit card processing outages with minimal disruption and maintain smooth operations.